You often see cables and wires lying around among your computers and other devices. One of them is probably a DVI cable. If you are unsure of what it is and what it does, all you need to know about it and more can be found in this article.
Digital Visual Interface (DVI) is a video display interface developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG). It is used to connect a video source, like a graphic card, to a display device, such as a computer monitor. In addition, it maximizes the quality of your LCD monitor and video graphics card.
DVI’s purpose was to create an industry standard for the transfer of digital video content. It replaces the previous Plug and Display (P&D) standard and is a level-up from the digital-only Digital Flat Panel (DFP) format for older flat panels.
The format of DVI’s digital video transmission is based on panelLink, which was developed by Silicon Image. panelLink uses a high-speed serial link referred to as Transition Minimized Differential Signaling (TMDS).
Besides DVI, there are other user visual interfaces like VGA and HDMI. Advanced technology and devices have mostly now settled on using the HDMI interface for high-definition media delivery. DVI is more focused on computers; however, you can still find it being used in consumer electronics, like TVs and DVD players.
Contents
What Are the Different Formats of DVI?
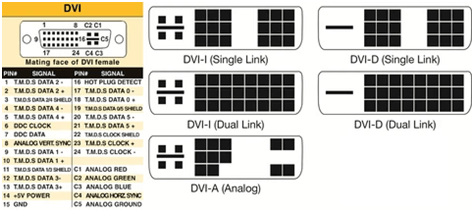
DVI cables come in three formats: DVI-A (analog only), DVI-D (digital only), and or DVI-I (digital and analog). Furthermore, they have two varieties: single-link and dual-link. Let’s look at their differences.
DVI Formats
- DVI-A carries an analog signal only. DVI-A connectors have 17 (12+5) pins and do not have a dual-link option. A cable like this is used to transmit a DVI signal to an analog display. One of the most common uses of DVI-A is to connect a DVI monitor to a VGA monitor since they have the same type of signal.
The quality of a digital-to-analog conversion is not as topnotch as a digital-to-digital one, which is why a digital signal is almost always recommended.
- DVI-D is used for direct digital connections between the source of the video and the computer monitor. Single-link DVI-D cables have 19 pins (18+1) and dual-link DVI-D cables have 25 pins (24+1).
This DVI format delivers a higher-quality image than analog.
- DVI-I includes pins for both analog and digital signals. With this format, you can have the best of both worlds, meaning this type of cable is capable of carrying both a digital-to-digital signal and an analog-to-analog signal. This is a more practical cable to buy because of its versatility.
A DVI-I single-link connector has 23 pins (18+5), while its dual-link connector has 29 pins (24+5).
It should be noted that digital and analog formats of DVI are non-interchangeable. This means that a DVI-D cable will not work when connected to an analog system, and a DVI-A will not work on a digital system.
Read on to learn the differences between single-link and dual-link DVI.
What Is a Single-Link DVI Cable?
The single-link DVI cable is a very simple and useful solution for digital displays. It has a single 165 MHz transmitter that can support resolutions up to 1920 × 1200 at 60 Hz. Single-link cables use only 12 of the 24 available pins in the DVI connector.

What Is a Dual-Link DVI Cable?
For dual-link connectors, higher resolutions of up to 2560 × 1600 can be supported at 60 Hz. This is because dual-link DVI doubles the number of TMDS pairs (that high-speed serial link mentioned earlier), which in turn doubles the bandwidth of the video. Dual-link cables make use of all 24 pins, and they are less common than single-links.

How Do You Know Which DVI Cable You Need?
It is crucial to determine what type of DVI cable your device requires so that everything can work properly. One of the first things to do is check both of the female DVI plugs to find out what signals they are compatible with.
- If one or both connections are DVI-D, then you need a DVI-D cable.
- If one or both connections are DVI-A, then you need a DVI-A cable.
- If both connections are DVI-I, a DVI-I cable is recommended.
- If one connection is DVI and the other one is VGA, and the DVI is compatible with analog, buy a DVI to VGA connector or a DVI/VGA adaptor.
- If one connection is digital and the other one is analog, they are not compatible with each other. If this is the case, you need to use an electronic converter like an analog VGA to a digital DVI/HDMI converter.
How Long Should Your DVI Cable Be?
The ideal length of a DVI cable is dependent on the pixel clock frequency. Generally, cables that are 4.5 meters or 15 feet long are good for display resolutions of up to 1920 x 1200. Longer cables reaching up to 15 meters or 49 feet are used for display resolutions of 1280 × 1024 or lower.
DVI cables that are made out of fiber optic cables are available in lengths of up to 100 meters, although they can be expensive.
For longer distances, it’s better to use a DVI booster. A DVI booster is a signal repeater that uses an external power supply. This device is extremely helpful to maintain a signal or to minimize its reduction.
Which Is Better Between DVI and VGA?
VGA or Video Graphics Array typically has blue connectors. VGA cables transmit an analog signal to an LCD or any computer monitor. The signals that it carries may differ a lot in terms of quality. This is usually because of the quality and length of the VGA cable itself.

In addition, VGA is less expensive than cables designed digital signals. When digital was first introduced, the improvement from analog was easily noticed by people. But, the picture and audio from analog remain outstanding.
DVI, on the other hand, can carry both analog and digital signals. Its primary difference from VGA is the picture quality and the way the video signals travel. DVI is considered to be an upgrade from VGA. It’s newer and provides a better, sharper display when compared to VGA. Moreover, DVI connectors are usually white.
Even though DVI is the successor of VGA, it may not yet be available in newer monitors. Therefore, you must determine the exact DVI cable you need to link your source to the monitor.
To easily compare DVI and VGA, you can refer to the table below.
| DVI (Digital Visual Interface) | VGA (Video Graphics Array) | |
|---|---|---|
| Display | Sharper and more precise display, which is more noticeable at higher resolutions; picks up less interference from the environment | The quality of the display degrades from digital to analog conversion and back, since an analog signal is susceptible to noise and electrical disturbances |
| Audio | Requires a separate audio cable | Requires a separate audio cable |
| Signals | Three types of cables, namely DVI-A that transmits analog signals only, DVI-D that carries digital signals only, and DVI-I that carries both analog and digital signals | Only carries analog signals |
| Compatibility | Can convert to other standard interfaces such as HDMI and VGA | VGA to DVI and VGA to HDMI converters are available |
| Specifications | Hot-pluggable; external, digital video signal; has 29 pins; both have female ports and male endpoints; usually a white cable | Not hot-pluggable; RGB analog video signal; has 15 pins; both have female ports and male endpoints; usually a blue cable |
| Price | More expensive | Cheaper |
Which Is Better Between DVI and HDMI?
When talking about DVI and HDMI, DVI is the older standard and the larger one between the two. A DVI plug is rectangular in shape, with a matrix of 24 pins in three rows, which makes it a little bulky. To the right of this matrix is a square that consists of four more pins.
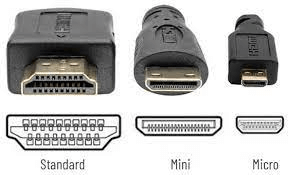
Meanwhile, an HDMI’s plug is much smaller than DVI. It is slim and compact and consists of 19 pins only. However, you can also get mini and micro versions of both DVI and HDMI.
DVI cables can only transmit video, while HDMI connectors transmit both audio and video signals. When it comes to display and picture quality, DVI and HDMI use the same system for digital video signals. Note that DVI does not support HDCP encryption by default, so it cannot be used to play full HD Blu-ray or other HD content.
Nowadays, HDMI is more common than DVI, especially when it comes to laptops, games consoles, TVs, and newer computer models.
The latest version of HDMI, the 2.1, can support a maximum data rate of 42.6 Gbit/sec. DVI only has a maximum data rate of 9.9 Gbit/sec. This means that HDMI can support resolutions of up to 4K at 144 Hz, or a very impressive 8K quality at 120 Hz when Display Stream Compression (a type of ultra-high definition display with reduced bandwidth demand) is utilized.
You can refer to the table below to see the similarities and differences between DVI and HDMI.
| DVI (Digital Visual Interface) | HDMI (High-definition Multimedia Interface) | |
|---|---|---|
| Display | Can support up to 1920 x 1200 HD video, but might not be able to play full HD Blu-ray or other HD content as it does not support HDCP encryption by default | Up to 4k and 8k resolutions at 144 and 120 Hz respectively; supports HDCP encryption |
| Audio | Requires a separate audio cable | Dolby Digital, DTS, DVD-Audio, Super Audio CD, Dolby Digital Plus, Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD High-Resolution Audio, DTS-HD Master Audio, MPCM, DSD, DST, LPCM |
| Signals | Three types of cables, namely DVI-A that transmits analog signals only, DVI-D that carries digital signals only, and DVI-I that carries both analog and digital signals | Carries purely digital signals; has five types, which are Types A to E (Types A and B are HDMI 1.0, Type C is 1.3, Types D and E are HDMI 1.4) |
| Compatibility | Can convert to other standard interfaces such as HDMI and VGA | Compatible with DVI and VGA with converters and adaptors |
| Specifications | Hot-pluggable; external, digital video signal; has 29 pins | Hot-pluggable; external, digital video and audio signal; has 19 or 29 pins |
| Price | More affordable | More expensive than DVI if they are from the same brand or manufacturer, but there are a lot of price variations due to many brands in the market |
FAQs
How Do You Recognize a DVI Cable?
By looking at the flat pin on one side of the cable, you will know whether the cable is digital or analog. A flat pin surrounded by four pins can be either DVI-I or DVI-A, while a flat pin by itself means that your cable is a DVI-D.
To know if a DVI cable is analog, single-link, or dual-link, you can look at the pin sets at one end. There are two separate 9-pin sets (rows of 6) for a single-link cable, whereas a 24-pin set (rows of 8) is a dual-link cable. On the other hand, a separated 8-pin and 4-pin set indicates DVI-A.
How Do You Connect DVI to HDMI?
You can easily connect DVI to HDMI by using an adaptor.
How Do You Connect DVI to VGA?
If your source is an analog DVI and you have a VGA monitor, then all you will need is a DVI-to-VGA adaptor. But if you have DVI-D as the source, you will have to get a DVI-D-to-VGA video adaptor. This converts the digital signals to analog data.
Summary
When shopping for a connector for your video source and your monitors, make sure to find out first what you need exactly. Do you need a VGA? An HDMI? Or a DVI cable? Now that you have read this article, you have an idea of what cable or connector you should purchase for your devices.
Conducting proper research will definitely help before buying since there are a lot of cables out there. Many might be similar in terms of quality, but their prices can also vary because of their specifications.





